MATH 222 In Class Exercises on Logarithms and Exponentials
1. Solve for x: ![]() . First solve this
using the properties of the natural logarithm function. Then graph the function
. First solve this
using the properties of the natural logarithm function. Then graph the function ![]() and see where it reaches
height 1. Finally use the solve function on
the calculator.
and see where it reaches
height 1. Finally use the solve function on
the calculator.
2. Let y = f(x) = xe-x. Find the first and second derivatives of f(x). Find the critical points and points of inflection. Sketch the graph of f(x) and check your sketch with the calculator.
3. Evaluate the
following integrals and check your answer on your calculator: ![]()
4.
Evaluate the integral ![]() by the following
method. Let F(x)=axe-2x+be-2x, where a and b are unknown constants. Find the derivative of F(x) and determine the
values of a and b that make the derivative equal to
the integrand xe-2x.
by the following
method. Let F(x)=axe-2x+be-2x, where a and b are unknown constants. Find the derivative of F(x) and determine the
values of a and b that make the derivative equal to
the integrand xe-2x.
5. Let ![]() Find a if f(2) = 2. (You should give an answer in terms of ln x and a numerical answer.)
Find a if f(2) = 2. (You should give an answer in terms of ln x and a numerical answer.)
Solutions:
1. ![]() Thus
Thus
![]() . This is a quadratic
equation. Solve using the quadratic
formula. There are two solutions:
. This is a quadratic
equation. Solve using the quadratic
formula. There are two solutions: ![]() . Only the positive solution,
. Only the positive solution, ![]() is in the domain of
both lnx and ln(x-1).
is in the domain of
both lnx and ln(x-1).
2. ![]() , The only critical point is x = 1. The only point of
inflection is x=2. F increases on (-¥,1] and decreases on [1,¥). f is concave up on [2,¥) and concave down on (-¥,2].
, The only critical point is x = 1. The only point of
inflection is x=2. F increases on (-¥,1] and decreases on [1,¥). f is concave up on [2,¥) and concave down on (-¥,2].
3. 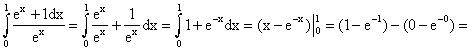
![]()
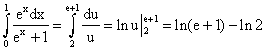
Let u = ex+1, du = exdx, if x = 0, then u = 2; if x = 1, then u = e+1.
4. ![]() If a=-.5 then
If a=-.5 then ![]()
We need to find b so that -.5-2b = 0 or b = .5/(-2).
Thus b is equal to .25. The integral is ![]() = -.5xe-2x +
.25e-2x + C.
= -.5xe-2x +
.25e-2x + C.
5. ![]()